Phases of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
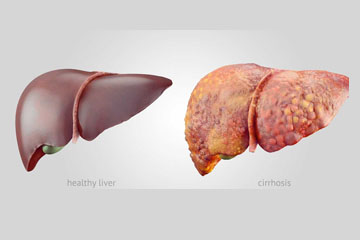
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as the same suggest is characterized by an excess of fat deposited in liver cells, in absence of significant alcohol intake.
NAFLD can also lead to serious consequences including Liver cirrhosis, Liver Failure, Liver Cancer, and Death due to Liver Failure.
Who is at a higher risk of developing Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease?
NAFLD is a fairly frequent condition that affects one out of every three to five people and one out of every ten children acrossthe world. In India its prevalence ranges from 8% in villages to 30% in metropolitans cities. Obesity is regarded to be the leading cause of fatty liver infiltration. According to some estimates, fatty liver affects around two-thirds of obese adults and half of the obese children. Another important risk factoris diabetes. Approx. 50-70% of patient with long standing diabetes have NAFLD and they don’t know about it. Patient who have high cholesterol are also an increased risk of NAFLD.
Types of Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease:
NAFL
NAFL(Nonalcoholic fatty liver) is a kind of Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease in which there is fat in the liver but little to no inflammation or damage to the liver. NAFL does not usually advance to the point of causing liver damage or problems. However, NAFL might induce discomfort due to liver enlargement.
NASH (Nonalcoholic fatty liver)
NASH(Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis) is a kind of Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease in which the liver is inflamed and damaged, as well as having fat in the liver. NASH can induce fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver due to inflammation and liver injury.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is typically a silent illness with little or no symptoms. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes are among the diseases that increase your chances of developing Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease. Unless you look for it these high risk conditions, you will miss it and patient will present later will complications.
If you have NAFLD, Dr. Ashish Kumar Jha– Gastroenterologist and Hepatologist in Bihar advises losing about 10% of body weight , if you areoverweight or obese, by a combination of exercises and right diet.
● Avoid meals and beverages that are high in simple sugars. Sweetened soft drinks, sports drinks, sweetened tea, and juices contain these sugars.
● Reducing your consumption of saturated lipids, which are heavy in calories and raise your risk of obesity
● Consuming more foods with a low glycemic index, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods have a lower glycemic index than foods, such as white bread, white rice, and potatoes.
● If you have Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease you should avoid drinking alcohol since it might worsen your already bad liver.
● In addition you should get your diabetes and blood pressure controlled, if elevated.
If you have fatty liver disease, you should educate yourself about it and cooperate closely with your liver specialist. Because many drugs might impair your liver, make sure to tell all of your doctors about any medications you’re taking.