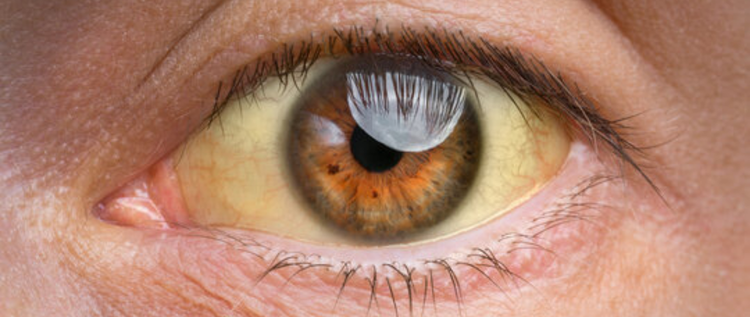
Jaundice, a condition commonly encountered in medical practice, is characterized by the yellowing of the skin and eyes. It occurs due to an excess buildup of bilirubin in the blood, a pigment formed by the breakdown of red blood cells. To shed light on this condition, let’s explore its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Causes of Jaundice:
Hepatitis: Viral infections (like hepatitis A, B, C, etc.) can lead to inflammation of the liver, impairing its ability to process bilirubin effectively.
Liver Cirrhosis: Long-term damage to the liver tissue, often caused by alcohol abuse or certain chronic diseases, can result in jaundice.
Obstruction: Conditions such as gallstones, tumors, or pancreatic cancer can obstruct the bile ducts, preventing the excretion of bilirubin into the digestive system.
Hemolytic Disorders: Inherited conditions or diseases that cause rapid breakdown of red blood cells can overload the liver with bilirubin.
Medications: Some medications and drugs can interfere with liver function, leading to jaundice as a side effect.
Symptoms of Jaundice:
Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes: This is the hallmark symptom of jaundice, caused by the buildup of bilirubin.
Dark Urine: Bilirubin can make urine appear dark or brownish in color.
Pale Stools: Reduced bilirubin excretion can cause stools to become pale or clay-colored.
Itchy Skin: Bilirubin accumulation can lead to itching in some individuals.
Abdominal Pain: Especially if jaundice is caused by gallstones or other obstructions.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Blood Tests: A simple blood test can measure levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes, helping to diagnose the underlying cause of jaundice.
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs may be used to visualize the liver, bile ducts, and pancreas to identify any obstructions or abnormalities.
Treatment: Treatment for jaundice depends on its underlying cause:
Hepatitis: Antiviral medications may be prescribed.
Liver Cirrhosis: Management focuses on treating the underlying cause and preventing further liver damage.
Obstruction: Surgical intervention or procedures to remove the blockage may be necessary.
Medication-related: Stopping the offending medication or finding an alternative may resolve jaundice.
Supportive Care: In many cases, supportive care such as adequate hydration, rest, and proper nutrition can aid recovery.
Conclusion:
Jaundice is a symptom of various underlying medical conditions affecting the liver or bile ducts. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in preventing complications and promoting recovery. If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms of jaundice, seeking medical attention promptly from professionals like Dr. Ashish Kumar Jha can make a significant difference in the outcome.
